Vital Signs Data
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG)
SDG 11.1: Ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing.

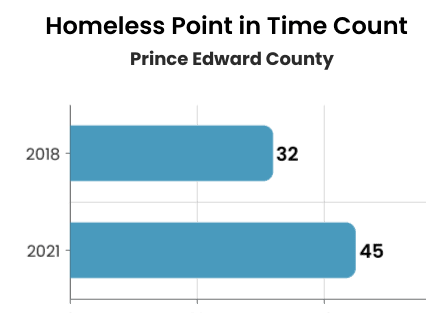
Unhoused Residents in our Community
Unhoused Residents in our Community
• Establishing a systematic approach for matching people to services and supports;
• Prioritizing offers of services, supports and housing to individuals as they become available; and
• Improving coordination and access to local programs, services and resources available for individuals experiencing homelessness.

Threats to Housing Stability
With the rising cost of living, half of Ontarions surveyed (50%) are just $200 away from financial insolvency. This is an increase of 7 points (YoY) since 2024. (MNP Consumer Debt Index)
Locally, in addition to soaring rental and inflation rates, “renovictions” are forcing out tenants as neighbourhoods undergo gentrification.
of Ontario residents surveyed are $200 away from insolvency
“More people are reaching out for support from eviction prevention and rental assistance programs, with many in danger of becoming homeless. Social assistance rates far below the poverty line and lack of technology access are barriers for the most vulnerable people who need to reach legal resources and communicate during COVID-19.”
Lisa Turik, Community Advocacy and Legal Centre
“More people are reaching out for support from eviction prevention and rental assistance programs, with many in danger of becoming homeless. Social assistance rates far below the poverty line and lack of technology access are barriers for the most vulnerable people who need to reach legal resources and communicate during COVID-19.”
Lisa Turik, Community Advocacy and Legal Centre
Causes of homelessness
Causes of homelessness
The causes of homelessness are complex and can be broken down into three categories: (homelesshub.ca)
- Structural factors, such as economic and societal issues that affect opportunities, environments, and outcomes for individuals. This includes poverty, discrimination, lack of affordable housing, and the impact of colonialism on Indigenous Peoples.
- Systems failures, where systems of support are inadequately delivered. Barriers to accessing public systems (health, social services, and legal supports), and failed transitions from publicly funded institutions (child welfare, hospitals, and corrections) are examples of systems failures.
- Individual and relational factors where personal circumstances, such as crises (like sudden unemployment or a house fire), mental health and addiction, housing insecurity, and interpersonal violence, can lead to homelessness.

